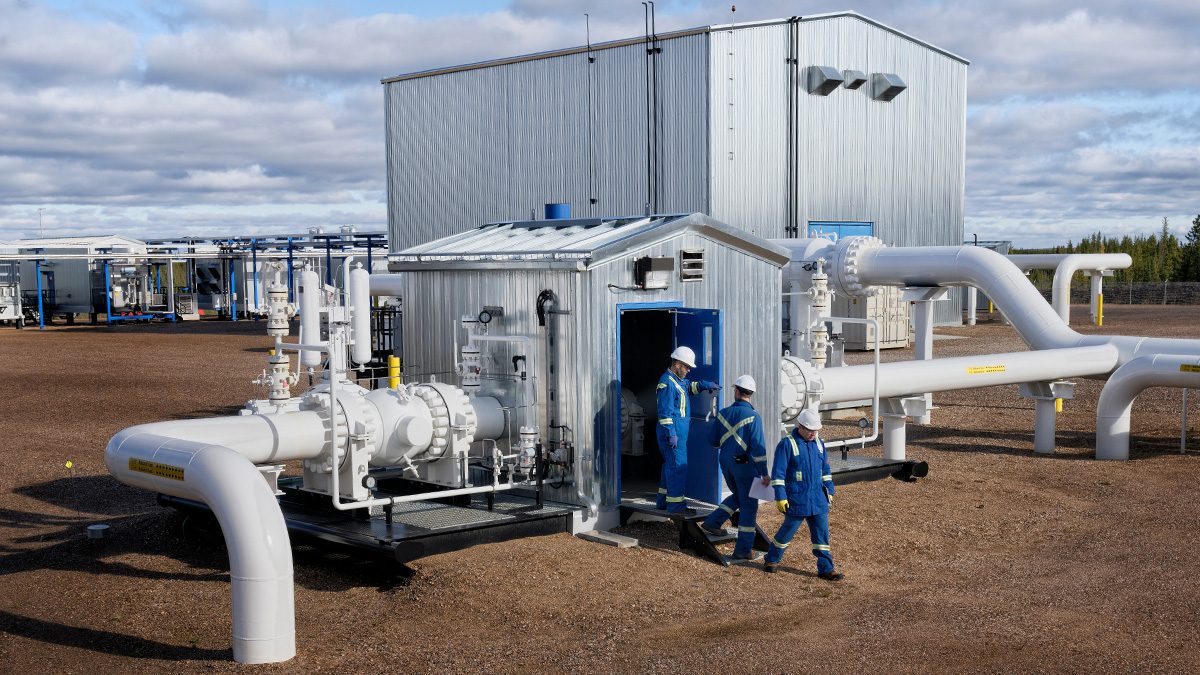
In a landmark agreement announced July 30, a consortium of up to 72 Indigenous communities in Alberta, British Columbia and Saskatchewan will buy a 5.34 per cent stake in TC Energy’s NGTL natural gas network.
The agreement is backed by a $1 billion loan guarantee from the Alberta Indigenous Opportunities Corporation (AIOC).
TC Energy’s sprawling NGTL network spans 25,000 kilometres and handles about 10 per cent of North America’s natural gas, connecting production in Alberta and British Columbia to domestic and export markets.
The loan guarantee has similarly impressive scope and size, quadrupling the AIOC’s previous largest financial commitment, a $250 million loan guarantee provided to 23 Indigenous communities in September 2022 to help purchase an 11.57 per cent stake in seven Enbridge oil sands pipelines in northern Alberta.
The deal will raise the AIOC’s support of Indigenous equity ownership in resource projects to over $1.68 billion since 2019.
“I’ve participated in three of these transactions, including the Enbridge loan guarantee, and you can see an evolution in the size and complexity of these agreements,” says Justin Bourque, founder and president of Âsokan Generational Developments, a consultancy that specializes in partnerships between Indigenous communities and industry.
“They are building on the good work from previous deals and it’s wonderful to see the AIOC expanding into neighbouring provinces, where these types of agreements will have significant benefits to the participating Nations in B.C. and Saskatchewan as well as Alberta.”
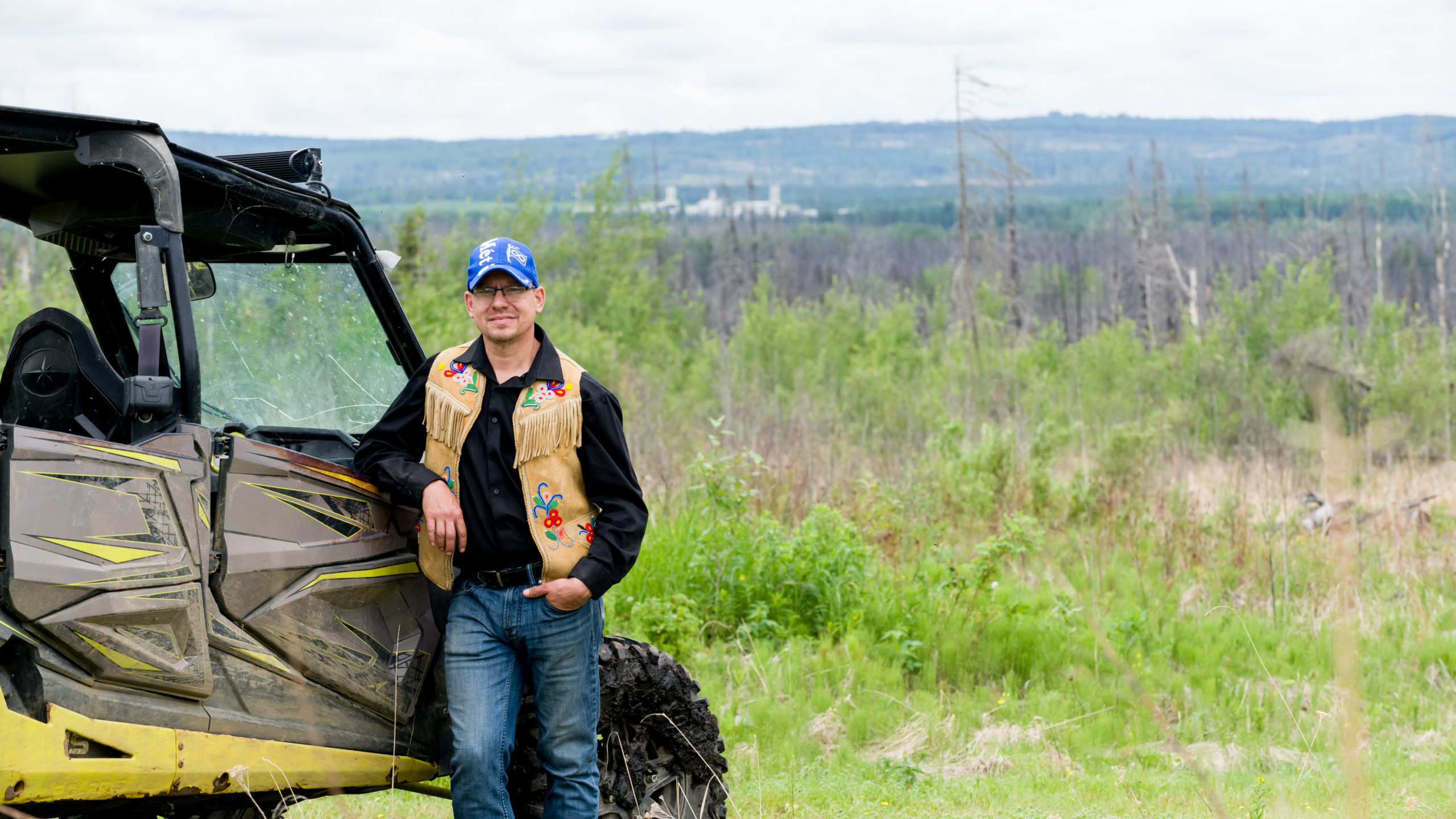

Âsokan Generational Developments president and founder Justin Bourque pictured on his trap line in northern Alberta with the Long Lake oil sands facility in the background. Photo for Canadian Energy Centre
The new agreement also demonstrates growing comfort among Indigenous communities, industry players and lenders as these equity arrangements become more commonplace, says Heather Exner-Pirot, director of energy, natural resources and environment at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, an Ottawa-based think tank.
“There are some formidable challenges with trying to negotiate with multiple communities across different treaty areas and provinces, but this shows the confidence the Alberta government has in backstopping these bespoke deals with communities and companies when the merits of the project deserves it,” says Exner-Pirot, who also serves as a special advisor to the Business Council of Canada.
“It also demonstrates the confidence from the lenders in these equity deals for pipelines. And that confidence is well founded because these existing pipelines are a stable business that generate the revenues to pay back the loan as well as income for the communities to use as well.”
The announcement builds on momentum for Indigenous ownership of Canadian energy projects, including June’s announcement that the Haisla Nation and Pembina Pipeline Corporation will move ahead with the Cedar LNG project.
The floating LNG export facility on Canada’s west coast will be the world’s first with Indigenous majority ownership.
Bourque sees the agreements providing a framework for future partnerships between Indigenous communities, government and industry beyond equity ownership.
“This is an important stepping stone in our evolution and it’s exciting to see it continue through pursuing opportunities in energy development, decarbonization and energy transition projects,” Bourque says.
“We are writing the history of tomorrow today, not living the outcomes of our forefathers.”
Exner-Pirot also sees a bright future for collaborations between Indigenous communities and energy companies, in part because the federal, Saskatchewan and BC governments now also offer loan guarantee programs.
“These deals take months, if not years, to come together and what this shows is the AIOC, Indigenous communities and energy companies have found a template that works,” she says.
“The NGTL loan guarantee is the biggest but it won’t be the last one.”
The unaltered reproduction of this content is free of charge with attribution to the Canadian Energy Centre.